Ever stopped to think about cement? It might seem like just a dull, gray, dusty powder or the glue that holds concrete together, but it’s time to set the record straight.
Cement is the unsung hero in the construction industry and beyond.
This stuff isn’t just vital for ready-mix concrete production. It’s the versatile powerhouse behind everything from concrete, mortar, and grout to pre-cast concrete pipe, bridge beams, a soil stabilizer, and more.
And it doesn’t stop there.
Cement even plays an important role in waste management.
Talk about a jack-of-all-trades!
So, What Exactly is Cement?
You might be wondering, “What’s it made of?”
Well, it’s a mix of calcined (that’s a fancy word for heated) lime and clay combined with water to create a paste that hardens over time. Think of cement as the glue that holds concrete together, binding the other ingredients into a solid, rock-like mass.
But it isn’t just a binder; it’s a multi-tasking maestro in the construction symphony.
How Versatile Is It, Really?
Cement is a versatile construction material that comes in various types, each possessing unique properties and uses. Among the main types of cement are:
- Ordinary Portland Cement (OPC) – A general-purpose cement suitable for most applications.
- Portland Pozzolana Cement (PPC) – A modified version of OPC, enhanced with pozzolanic materials to provide resistance against chemical erosion.
- Rapid Hardening Cement (RHC) – Ideal for projects requiring quick set times, such as roadways and pavement construction.
- Sulphate Resisting Cement (SRC) – Recommended for foundations, pilings, aquatic projects, and sewage works in high-sulphate environments.
How Does Cement Become Concrete?
Here’s where it really shines: turning it into concrete. It starts with cement, water, sand, and aggregates (like gravel or crushed stone). Mix ’em all together, and you’ve got the beginnings of a hard, durable material.
But the real magic?
That happens when water meets cement. This sparks off a chemical reaction known as hydration, transforming the mix into a hardened hulk that can take on heavy loads and tough weather conditions.
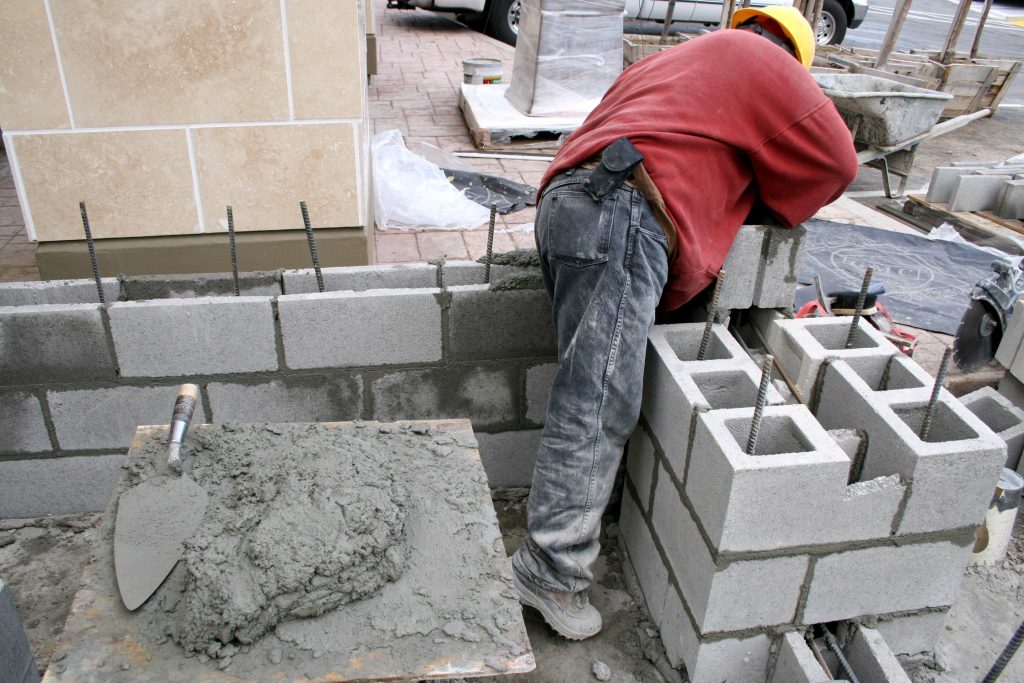

What’s Its Role in Mortar and Grout?
Beyond concrete, cement is the secret sauce in the creation of mortar, that sticky paste that bonds bricks, stones, and other masonry units together.
With a simple recipe of cement, sand, and water, mortar is formed. It’s like the spread in a sandwich, filling the gaps between bricks or stones and keeping everything tightly packed.
Still think it’s just for concrete and mortar?
Think again.
This versatile superstar extends its reach to other areas of construction too. Take grout, for example. Cement is used to produce this fluid form of concrete that fills gaps and seals joints, ensuring structures stay tightly sealed and structurally sound.
How is Cement Used in Soil Stabilization?
Glad you asked! It isn’t just used above ground—it’s also used below the surface in a process known as soil stabilization.
You see, not all soils are suitable for building. Sometimes soil needs a little help, and cement is up for the challenge.
By mixing it with loose, partially unstable soil, you can create a stronger base for roads, bridges, and other infrastructure. Adding cement improves the soil’s bearing capacity, which is another way of saying it makes soil stronger so that it can support a load.
And that means using cement for soil stabilization is yet another example of how it helps lay the foundation for successful construction projects that would otherwise never get off the ground.
What Else Can You Do With It?
So we’ve established cement’s got chops. But how else can contractors use it?
Well, beyond its starring role as the binding agent in concrete, it plays an integral role in producing grout and pre-cast concrete parts like panels, beams, stairs, pipes, and tunnels.
But wait! There’s more!
It even moonlights in the waste management industry too.
How Is Cement Used in Waste Management Industry?
Portland cement and cement products like grout are often used fill and to seal off hazardous waste in abandoned drilling and mining operations. Site remediation contractors also rely on it to stabilize and solidify waste materials to create safe and reliable landfills.
Another novel use for cement is as an underground barrier trench. By mixing together a slurry of cement and bentonite clay, contractors can inject the solution into the soil, creating cutoff walls. These cut-off walls contain the horizontal flow of water, fluids, and hazardous materials that would otherwise contaminate nearby soils, wetlands, and watersheds.
But that’s not all!
Soil-cement, a composite material of soil, cement, and water, hardens into a sturdy, durable substance. The result is a foundational material suitable for pavement base, slope protection, and as a liner for wastewater treatment lagoons, sludge drying basins, ash settling ponds, and other waste containment facilities.
Cement wears many hats in the construction world beyond being the glue that holds concrete together.
So, Just How Useful is Cement?
As you can see, it’s one of the most versatile and widely used materials in construction and a force to be reckoned with.
Cement has been valued for its remarkable strength, durability, and versatility for a long time. It is a crucial element in construction, as it is used to create concrete and bind bricks with mortar. Moreover, it is utilized to seal gaps with grout and stabilize soil, making it an essential component in almost every aspect of construction.
Therefore, it would be fair to say that cement plays a crucial role in constructing the world around us.
From creating concrete and binding bricks with mortar to sealing gaps with grout, stabilizing soil, and protecting the environment, cement is a key player in nearly every aspect of construction.
So next time you see a building, roadway, landfill, or retention basin, remember: beneath every great structure lies great cement — literally!